It’s important to make informed choices. Companies that leverage go-to-market intelligence outperform companies that rely on intuition or stale data.
What makes intelligence actionable compared to the data that most companies acquire?
The difference lies in how intelligence information is obtained, analyzed, and transformed into strategic actions.
In this article you'll learn the basics of go-to-market intelligence, see the different forms it takes, and best of all, learn how to use that information to drive significant business results.
What is go-to-market (GTM) intelligence?
Go-to-market (GTM) intelligence is the process of collecting and analyzing market, competitor, and customer data to guide product launches and business strategies. Unlike traditional market research, GTM intelligence focuses on actionable insights like customer pain points, competitor positioning, and real-time market trends to drive revenue growth.
GTM intelligence like this dictates direction and implementation, as opposed to traditional market research.
Questions GTM intelligence-hounds ask are:
- Who are the perfect clients for our product or service?
- What foils and frustrates them?
- What is the process by which people decide to buy?
- Where can I find them and how do I reach them?
- Which message will be most compelling?
- What white space exists and how are other companies positioning themselves?
Actionable go-to-market (GTM) intelligence uncovers different trends and opportunities to reveal the right strategic insights.
It includes quantitative stats like market size, growth rates, competitive positioning as well as qualitative context like customer preferences, how they buy, emerging trends.
Expert Perspective: "In rapidly evolving markets like those across Southeast Asia, GTM intelligence serves as both compass and radar—it tells you where to go and what obstacles lie ahead. Without it, companies are essentially navigating blindfolded." — Mari Elka Pangestu, Ph.D., Former Minister of Trade of Indonesia and Managing Director at World Bank
GTM Intelligence Development
Market intelligence isn't new, but its application has evolved over the last decade. Market intelligence used to be dependent on historical data and extensive market research, and information was often outdated by the time it reached decision makers.
Some of the latest go-to-market (GTM) intelligence comes in these forms:
- Real-time Tools: Using tools that can read the markets as they’re trending right now.
- Predictive Analytics: To predict trends before they even take off with the help of advanced analytics.
- Multiple Data Sources: Using different types of data, both internal and external.
- Context Data Interpretation: The data is analyzed in the context of the business and the industry.
What tools are used for GTM intelligence?
Top GTM intelligence tools include:
- SEMRush (competitive analysis)
- HubSpot CRM (customer behavior tracking)
- Tableau (market trend visualization)
- Sprinklr (real-time sentiment analysis).
GTM Intelligence Tools Comparison Table
| Tool | Primary Focus | Key Features | Best For | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEMrush | Competitive & Market Intelligence | Keyword tracking, backlink analysis, competitor traffic insights, market positioning | Digital marketing teams needing competitive visibility | $119-449/month |
| HubSpot | Consumer Intelligence | Customer behavior tracking, lead scoring, engagement analytics, sales pipeline analysis | Organizations with integrated marketing and sales functions | $45-3,600/month |
| Crayon | Competitive Intelligence | Real-time competitor monitoring, marketing change detection, battle cards automation | Sales enablement and competitive positioning | $500-1,200+/month |
| Tableau | Data Visualization | Interactive dashboards, multi-source data integration, predictive analytics | Organizations with complex data visualization needs | $70-840/user/month |
| Ahrefs | Market & Competitive Intelligence | Content gap analysis, market opportunity sizing, search volume tracking | Content strategists and SEO specialists | $99-999/month |
| Sprinklr | Consumer Intelligence | Social listening, sentiment analysis, consumer trend identification | Enterprise brands managing multiple market segments | Custom pricing |
| Klue | Competitive Intelligence | Competitor battle cards, intel sharing, sales enablement | B2B sales organizations with complex competitive landscapes | $300-1,000+/month |
| SimilarWeb | Market Intelligence | Market share analysis, audience insights, channel strategy | Market researchers and business development | $125-1,500+/month |
Indonesian Market-Specific Tools
| Tool | Primary Focus | Key Features | Local Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snapcart | Consumer Intelligence | Real-time purchase behavior, Indonesian consumer panel | Specialized Indonesian consumer insights with regional segmentation |
| Kalodata | Competitive Intelligence | Local competitor tracking, Indonesian market positioning | Indonesian language processing and local brand coverage |
| Ada Insights | Market Intelligence | Market sizing for Indonesia's emerging sectors | Specializes in Indonesia's tier 2-3 city growth metrics |
| DXT360 (dataxet:sonar) | Consumer & Competitive Intelligence | Local sentiment analysis, Indonesian media monitoring | Comprehensive coverage of Indonesian social and traditional media |
How Data Visualization Transforms GTM Intelligence
The power of data visualization in GTM intelligence: Turning raw GTM intelligence into visual forms accelerates decision making by orders of magnitude and increases the quality of decisions made. Aberdeen Group * 28% greater likelihood that users are able to find needed information with visual data discovery tools compared to those who do not.
Key visualization techniques for GTM intelligence include:
- Strategic Dashboards: Real-time monitoring of KPIs, market trends and competitive positioning that executives can review daily
- Customer Journey Maps: Graphical presentation of touchpoints and decision factors during a purchase
- Market Opportunity Heat Maps: Color-coded graphics that visualize market penetration and growth opportunities per segment
- Competitive Positioning Charts: Perceptual maps that show brand positioning against competitors
“Visualization reduces the time it takes to act on GTM intelligence by 44%, enabling teams to recognize and take advantage of market opportunities before the competition does,” notes Edward Tufte, data visualization expert and author of “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information."
Solutions like Tableau, Power BI and Looker are increasingly part of the GTM intelligence toolkit, which transforms confusing market and customer data into clear visual stories that create alignment and action.
The Core of GTM Intelligence
Picture a world in which real-time consumer desires, competitor placement, and untapped opportunity color every campaign, pricing decision, and sales pitch.
This is what GTM Intelligence foresees. It’s the process of gathering, analyzing and utilizing data including information from consumers, marketplace conditions, what competitors are doing and an organization’s own performance metrics to make decisions.
Unlike old market research, actionable go-to-market intelligence enables sales people to close more deals, marketers develop relevant messages, and product executives to prioritize market-relevant features.
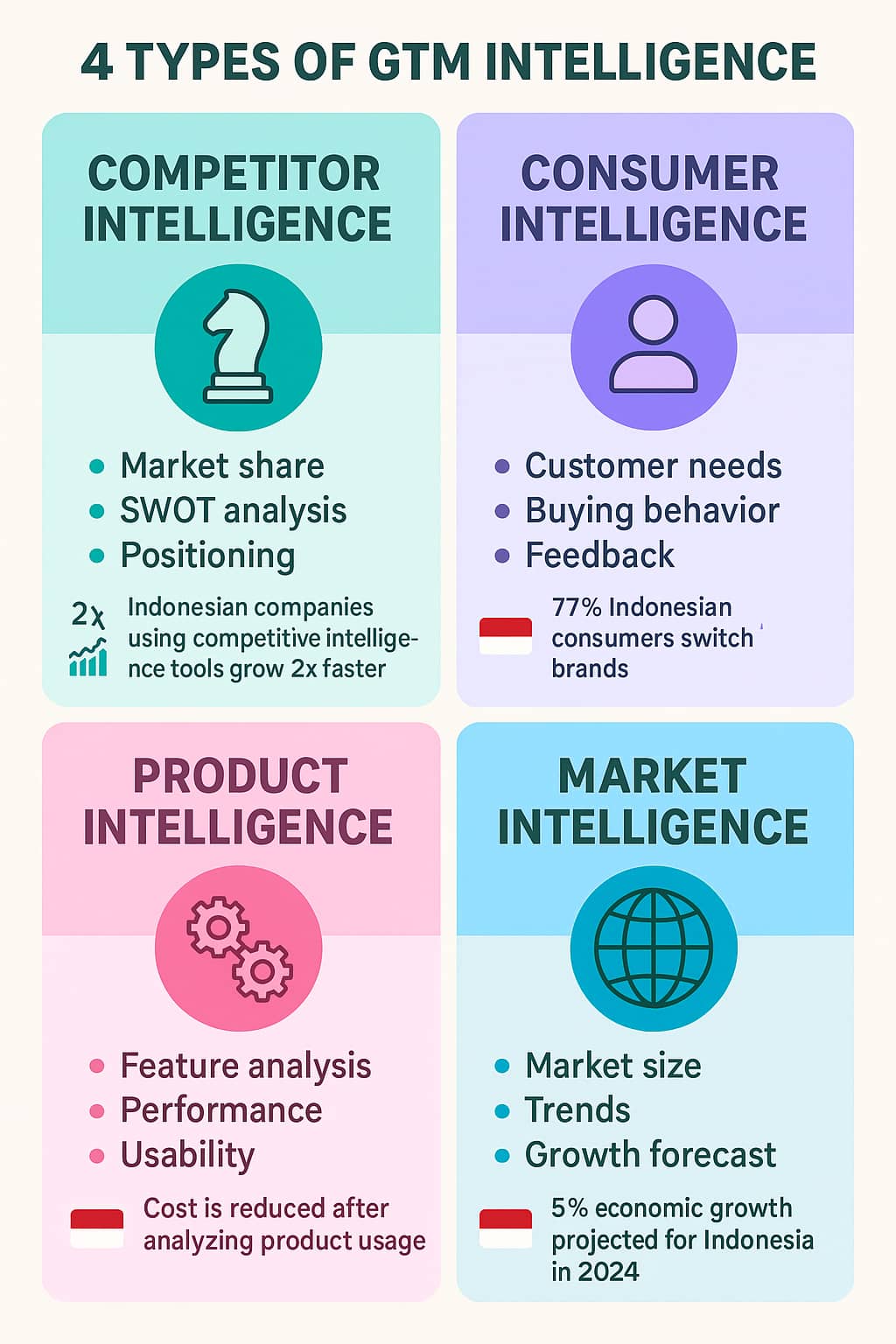
What are the Four Types of Market Intelligence?
There are four types of go-to-market data. They all have different purposes, but together they make up a complete system of intelligence.
1. Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence focuses on understanding your rivals' goals, strengths, weaknesses and likely moves.
This knowledge is then used to recognize market positioning threats and differentiation chances.
Some of the main aspects of competitive intelligence are:
- Competitor Mapping: Who are my direct and indirect competitors across different market sectors.
- Examining Competitors: Analyze their products/services, pricing strategies, and value propositions.
- Positioning Strategy: Identify how brands are positioned in the market.
- SWOT Analysis: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of competitors.
- Tracking Development: Watch the expansion plans of competitors, newcomers and recent acquisitions.
A software vendor can track competitors’ product introductions, price changes and customer sentiment to identify potential feature gaps or pricing opportunities.
This information can be used to guide product development and marketing.
Indonesian companies using competitive intelligence tools grow 2x faster in e-commerce. Platforms like Ripple10 or DXT360 (dataxet:sonar) provide real-time competitor tracking tailored to local markets.
— Tessar Napitupulu, Digital Marketing Expert (Arfadia)
2. Consumer Intelligence
Customer intelligence aids in understanding what your customers demands, actions, preferences, and decision making process looks like. Key components include:
- Creating Client Personas: This is where you develop rich profiles of who your ideal consumers are.
- Observing the Customer Journey – This means tracking the customer’s journey from awareness to purchase and all the way through to advocacy.
- Need Assessment: What are the obvious and invisible problems of the consumer?
- Consumer purchase Decisions: Illuminating when and why people buy.
- Structured Collection & Analysis of Customer Feedback: Including Voice of the Customer (VOC) Capture & Analysis.
3. Product Intelligence
Product intelligence analyzes how your products compare to your competitors and how your customers perceive them.
This intelligence drives where and how products need to be positioned, developed and optimized.
Key product intelligence components include:
- Feature Benchmarking: Ranking products based on the features they offer relative to the competition and customer demand.
- Performance Analysis: Bench testing of products in real world applications.
- Usability Info: Insight into how all users feel about your site and its functions.
- Perceived value versus Price sensitivity – Comparing perception of value across the segments of the market and price sensitivity across them.
- Features Usage Monitoring: Monitoring with the product features are more enjoyed and widely used.
For instance, a manufacturer could leverage product intelligence to learn that consumers seldom use expensive features.
This information allows them to reduce costs and optimize manufacturing while keeping customers happy.
4. Market Intelligence
Market intelligence is the overarching context for making business decisions, here is where you step back, look at the dynamics in the market, trends and environment that could affect your go-to-market strategy.
Critical Aspects of Market Intelligence are:
- Marketing Sizing and Segmentation: Determining the size of the target market and the critical customers.
- Growth Forecasting: Predicting market growth and where the opportunity lies.
- Trend Analysis: Knowing new-screen fashion between industry, consumer and technology.
- Legal & Compliance Tracking: Monitoring of all regulatory issues impacting market access as well as the global regulatory environment.
- Economic Conditions: Studying potential drivers of demand and purchasing power.
Energy companies could rely on market intelligence to identify changes in regulation at the state-level that can enhance demand for renewable energy.
This enables the company to concentrate its market expansion in some industries through tailored solutions that meet new requirements.
What are the 4 types of market intelligence?
The four core types of market intelligence are:
- Competitive Intelligence (analyzing rivals’ strategies)
- Consumer Intelligence (understanding buyer behavior)
- Product Intelligence (benchmarking features/usability)
- Market Intelligence (tracking industry trends/regulations).
Turning Knowledge into Action
Per Indonesia’s Ministry of Cooperatives (2023), SMEs adopting GTM analytics saw 35% sales growth within 6 months. Source : https://ojs.uajy.ac.id/index.php/kinerja/article/download/9519/3963
Valuable GTM intelligence directly informs strategic decisions, product development, marketing execution, and sales optimization—translating raw data into measurable business impact and competitive advantage.
Go-to-market intelligence is only useful to the extent that it results in a strategic action, not data. Here’s how firms translate intelligence into concrete business results:
1. Decision Making and Strategy Development
As companies make tough decisions, they need actionable intelligence. And strategic decision making and planning rely on it.
It enables leaders to make decisions on when to enter new markets, where to allocate resources, and which investments will bear the most opportunity for long-term success.
It also tells organizational structures that teams will have the abilities to overcome future roadblocks. It focuses on potential threats and helps decision-makers predict threats and devise mitigation strategies.
Intelligence finds real growth prospects beyond risk management. It must be smoothly integrated into the company's planning cycle to maximize its potential. Incorporating insights into formal strategy processes can turn raw data into a dynamic framework that drives crucial choices.
2. Innovation and Product Development
Effective product intelligence includes a composition of different data types, which could be about one-quarter numeric, half categorical, and one-quarter free text.
Intelligent product development and innovation turn raw market data into consumer-centric goods. This approach incorporates market data into all phases of product design and deployment, to ensure that products are dynamic solutions rather than static commodities.
Product roadmaps are designed to anticipate future points of need and constraint. Features solve specific customer problems.
Companies can balance profitability and customer satisfaction by pricing products according to both production costs and the perceived value to customers.
Brand positioning is a crystalized story that separates a brand apart from its competition by way of clarity and intent.
Innovation focuses on high-leverage areas where there are market gaps and invention can uniquely push forward needed change.
Firms that combine intelligence and action impact their industry by using data to not merely make incremental improvements, but completely reimagine the market landscape.
3. Execution and Stragegy of Marketing
Targeted intelligence transforms innovation into precision marketing. Relevant messages tied to segment values and pinpoint pain points deepens brand-consumer relationships.
Behavioral data is used to select channels that reach viewers within their preferred environments.
Content strategies extend beyond storytelling to meet the information needs and interests of specific audiences.
Leading marketing organizations employ real-time campaign analysis and continuous scouting for insights. It's this feedback loop that sharpens the edge of their smarts, enabling course-corrections to be made, on spending, on timing, on content, on channels, and on messaging.
You might also like :

4. Sales Enablement & Optimization
Today's sales effectiveness has three truths: it's formed at the front-line; it gets enabled through sales enablement; and it is optimized by intelligence transforming raw inputs into strategic stepping stones.
Building robust consumer profiles that indicate purchase intent is the bedrock of this space. These profiles reveal what’s driving consumers — and what’s holding them back.
Battle cards are produced to aid salespeople in defeating the competition. These are the tools that provide them with the specific data and rejoinders to fight comparisons with rivals.
Pricing methods should be flexible according to a combination of factors: profit margins, production costs, and competitors' price strategies.
The sales process needs to be aligned with the customer decision-making journey, from initial awareness through to final purchase decision.
Equipped with these tools, sales teams are able to not only shepherd buyers through the purchase process, but turn them into lifelong customers.
How does GTM intelligence improve decision-making?
GTM intelligence transforms raw data into strategic actions by:
- Identifying untapped market opportunities (e.g., feature gaps).
- Predicting customer demand shifts using real-time analytics.
- Enabling agile pricing and messaging based on competitor moves.
GTM Intelligence Implementation – Insight to Action Roadmap
Operationalizing a working GTM intel machine means it is something done systematically. And here is a roadmap to building your GTM intelligence capabilities:
Phase 1: Laying the Foundation (1-2 Months)
- Inventory existing avenues of intelligence and knowledge gaps
- Develop critical intelligence issues and questions in consonance with strategic goals
- Develop an organization framework and responsibilities for intelligence collection
- Choose and utilize foundational technology stack for data science and analysis
- Mistake : Attempting to gather too much data with no focus
Phase 2: Building operational capabilities (2 -3 months)
- Develop methods and model for intelligence synthesis.
- Educate relevant personnel on the use of intelligence.
- Maintain consistent intelligence briefing tempo for decision-makers.
- Develop feedback loops to sharpen focus of intelligence areas.
- Required resources include an intelligence analyst (0.5 FTE) and an executive sponsor.
Phase 3: Integration (3-4 Months)
- Embed intelligence inputs in critical decision processes (product roadmap, marketing plan, sales strategy)
- Build intelligence based decision models for common use cases
- Build out automated intelligence dashboards for key stakeholders
- Compile metrics to quantify how intelligence impact business results
- Mistake: No linkage of intelligence to particular decision points
Phase 4: Optimising (continuing)
- Quarterly intelligence impact assessments shall be carried out
- Improve techniques for the collection and analysis of data according to utility
- Extend intelligence to neighboring markets or areas of decision making.
- Leverage advanced analytics to create predictive intelligence capabilities
- Resource Estimates: Intelligence team (1-3 FTEs based on company size) with business analyst support
"The most common reason GTM intelligence initiatives fail is not poor data quality but poor integration with decision processes," notes GTM intelligence expert and author Geoffrey Moore. "Intelligence that doesn't influence decisions is merely interesting, not valuable."
Exceeding Legacy Approaches with Actionable GTM Insights
Actionable go-to-market (GTM) insights are a competitive advantage. Decisions makers in business will need to ask themselves whether they can afford to ignore the sound of good go-to-market intelligence.
Businesses that possess and analyze market data will outperform ones that continue to rely on old methods or gut instinct.
GTM intelligence will enable companies to structure market info, customer perspective and adjacent competitive dynamics into a revenue growth plan. A GTM intelligence system offers tactical, actionable analytics for teams who want to immediately improve their communication and competitive positioning.
Real-World Examples of GTM Intelligence In Action
Case Study 1: Transforming a B2B SaaS Company The challenge A healthtech company had previously failed to meet its goals when working with traditional go-to-market strategy consulting firms. They were determined to find a partner that would be as invested in their success as they were themselves.
Workday turned its market approach around when the enterprise software company executed an integrated GTM intelligence program. By integrating CI with the analysis of the customer journey, they were able to uncover an enormous window in the mid-market players who were offering insufficient onboarding experiences.
Results:
- Mid-market conversion rates up 34%
- 28% shorter sales cycle period
- 47% increase in first year customer retention
- $13.2M of incremental annual recurring revenue
"Our GTM intelligence program, fundamentally changed our approach to the market,” says the CMO of Workday. “Instead of making decisions based on hunches, we’re now armed with real-time intelligence to make course corrections and seize gaps in the competitive terrain.”
Case Study 2: Entering the CPG Market
When Unilever was looking to penetrate the Indonesian natural personal care market, it encountered deep-rooted local competitors supported by loyal customer bases. Drawing on extensive GTM intelligence including market, consumer, and competitive information, they :
Results:
- Developed a good insight into underserved consumer segments with 2.3x more price elasticity
- Articulated a positioning that spoke to a set of cultural needs that the competition were not addressing.
- Attained 23% market share in 18 months which was 40% above target
- Success to have set prices 15% higher than the average category and still grow
“The quality of our intelligence made all the difference,” says the RMD. “Instead of trying to base our product and marketing on generic market research, this GTM intelligence program had been able to uncover consumer pain points and competitive blind spots that our competitors had overlooked.”
Case Study 3 : Healthcare Technology Market Expansion Medical technology company Philips used GTM intelligence to expand its healthcare IT solutions in Southeast Asia. By systematically analyzing regulatory environments, competitive landscapes, and provider needs across different countries, they developed a comprehensive market entry strategy.
Results:
- Prioritized battlefield sequence (quantified opportunity scoring) for market entry
- Developed country-configured value propositions in response to distinct local healthcare delivery challenges
- 42% reduced time-to-revenue for expansion in target markets vs. previous expansions
- Lowered cost of customer acquisition by 38% with precise targeting
Through our GTM intelligence framework, we were able to confidently make data-informed decisions on where and how to enter these intricate healthcare markets,” says their VP of Strategy. “This kind of precision reduced our risk and accelerated our growth."
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is go-to-market intelligence, and how is it different from market research?
Growth and Retention—For Strategic and Product ‘Go To Market’ (GTM) A customized methodology to gather, analyze & apply data into decisions regarding when and how to launch product or service. Rather than the more general Market Research, GTM intelligence provides actionable insight into the market entry and expansion strategies.
GTM intelligence fuses hard data points – market size, growth rates – with softer touchpoints to customer wants and buying behaviour in order to reveal deeper currents within the market and opportunities that can help underpin strategic decisions.
2. What are four types of market intelligence that businesses need to develop?
The components of a full intelligence system are four basic kind of market intelligence:
- Competitive Intelligence - Learning what your competition is doing right and wrong
- Consumer Insight—understanding the needs, wants, and decision-making of target consumers
- Product Intelligence: does the comparison with competitors and the perception of your products by customers; and
- Market Intelligence—exploring macro market dynamics, trends, and environmental variables that impact your go-to-market.
3. How can organizations transform go-to-market intelligence into real-world business results?
These companies turn go-to-market insights into measurable business results with four primary methods:
- Decision Making & Strategic Planning to Monitor Markets, control resources and manage risk with intelligence-led approach to entry decisions
- Innovation and Product Development, integration of market knowledge in to product design leading to consumer centric solutions
- Execution and Marketing Strategy—creating personalized communications and selecting the right channel on the basis of the customer’s behavior; and
- Sales Enablement—ensuring that sales teams have detailed customer profiles, battle cards for competitive selling and competitive price strategies that reflect the value of the product they’re selling.
Author bio:
Rizky Darmawan is a marketing digital and research nerd who helps brands (and his baby son) grow with fresh strategy and a creative show of force. When he’s not sifting through possible brainstorming ideas, you’re most likely to find him tending to his small garden in his yard. Hang out with him on https://www.linkedin.com/in/rizkyerde/

